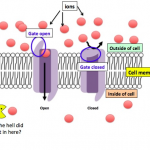
One thing that we know for sure is that the “you use it, you lose it” law of antimicrobial resistance rules. This means that the use of antibiotics -- whether appropriate or not -- will select for the emergence of resistant pathogens. Therefore, we can expect an increase in bacterial resistance in our hospitals – globally.
Drugs & Pharmaceuticals
Virtually every day there's news about one or more clinical trials in progress or being planned. But most people don't fully understand what the different trials mean. ACSH advisor Dr. Katherine Seley-Radtke gives us a primer that clearly explains the entire process. Timely reading.
Somehow a drug has turned into a political tool. This is nuts. Hydroxychloroquine may or may not end up having any utility as a COVID-fighting drug. But its cardiac toxicity is real, unlike the nonsense surrounding it. Let's stick to the science: Torsades de pointes, not talking points.
Is sticking your finger down your throat a pleasant experience? How about sticking it down there and leaving it for three weeks? You probably wouldn't want to be awake for that, but a shortage of IV hospital drugs is causing some real problems for intubated patients on ventilators. And guess what drug they're out of? Fentanyl(!). And if you read on you'll get that, plus a bubble bath with Kim Jong-un, all in one idiotic article.
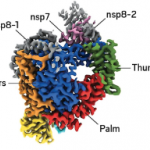
Drugs that don't work when taken orally are the bane of drug discovery chemists. Now it's the bane of the world. But there are techniques that can convert orally inactive drugs, like remdesivir, into pills. Here's how they work.
Remdesivir arrived with great hope and even greater expectations. Would this drug finally awake us from the 2-plus-month long nightmare that has the U.S. tossing and turning in its sleep? As things stand now that answer is no. Here's why.
Remdesivir appears to be our first promising treatment for COVID-19. It is certainly neither a cure nor a preventative. But it seems to reduce the length of hospital stays, and thus, increases the health systems’ capacity by about a third. So if you were in charge of selling this drug, what price would you set?
Sometime, hopefully in the not too distant future, we will need to look at how this tragedy unfolded and come to grips with what we could have done to make it, at least, somewhat less tragic. The fact that several countries and societies were able to escape the worst of the pandemic provides us with opportunities to learn and to act.
After months of speculation, the results of the first placebo-controlled trial of remdesivir are out. The drug does help people with COVID-19 disease, but it's nothing to get excited about. Here's why.
The first data from the SIMPLE trial of remdesivir has been released by Gilead. Even though this is the first complete trial of the drug, it doesn't answer many questions. That's because there was no control group – something that would have been unethical for the trial participants since they had severe disease. We're just getting started.
It's only one trial, and we don't even know if the report is correct. But a leaked draft report indicated that remdesivir was ineffective in its first controlled trial. Let's assume that this is true and we see the same from other trials. If so, this will not simply be another experimental drug failing. It will be deeply disturbing. Here's why.
Preliminary data, obtained from a randomized clinical trial of remdesivir in China, look bad. Maybe even very bad. But this doesn't mean that the drug won't be shown to be useful in other trials. Nonetheless, not good news.